1. Introduction a) Background of the study
ocial media is computer-based technology that facilitates sharing of ideas, thoughts, and information through the building of virtual networks and communities. By design, social media is internet-based and gives users quick electronic communication of content. Content includes personal information, documents, videos, and photos. Users engage with social media via computer, tablet or smartphone via web-based software or web application, often utilizing it for messaging (Cohen, 2011).
Social media originated as a tool that people used to interact with friends and family but was later adopted by businesses that wanted to take advantage of a popular new communication method to reach out to customers. The power of social media is the ability to connect and share information with anyone on Earth as long as they used the social media(Icha Oyza and Agwu Edwin, 2015).
According to (Aaron Smith and Monika Anderson, 2018) it has been estimated that some 81% of Americans used social media as of 2017, and even increases time to time. According to one estimate; over one-fifth of an individual's online time is spend on social media. In 2005, the percentage of adults using social media was around 5%. Globally, there are roughly 1.96 billion social media users. That number is expected to rise to 2.5 billion by the end of 2018. Other estimates are even higher. According to the Pew Research Center, social media users tend to be younger (some 90% of people ages 18 to 29 used at least one form of social media), better educated and relatively wealthy.
The increased use of social networking websites has become an international phenomenon in the past several years. What started as a hobby for some computer literate people has become a social norm and way of life for people from all over the world (Flad, 2010). Teenagers and young adults have especially embraced these sites as a way to connect with their peers, share information, reinvent their personalities, and showcase their social lives (Belal, 2014). With the increase of technology used for communicating with others and the popularity of the Internet, "Social Networking" has become an activity that is done primarily on the Internet, with sites like Myspace (Bebo, 2017).
Facebook is the most popular social networking website on the internet today, with more than 500 million members worldwide. This is rather interesting story of an unassuming 19-years-old who did not realize the true potential of what he was setting out to accomplish. Mark Zuckerberg, born May 14, 1984, in New York, was a sophomore in Harvard University when he stumbled upon this marvelous creation that made him a millionaire within a few years (Boyd, 2018) .
Facebook being at the forefront of the social media craze, has over 500 million active users on its website every month. It is emerged on February 4, 2004, when a 19-years-old sophomore Harvard student named Mark Zukerberg founded the revolutionary site to connect Harvard University students (Grossman, 2010). But later, this site allows users to build social networks with hundreds or even thousands of people around the world of which university students are one of the primary demographics using Facebook, with features such as photos, wall posts, and status updates becoming seemingly irresistible to those who want to connect with their friends (Hossain, 2017).
Many students who have access to social media waste their time on it by chatting and surfing the internet for non-educative information. They are glued to their phones all day, making them a loose sense of time. Some students are also seen pressing their phones during classes, seminars, and also in the libraries. Some of them will even plug in their ear pieces and hum out the songs they are listening to when studying which reduce their rates of assimilation and act as a source of disturbances to others around them (Ictech, 2014).
In a bid to know what is going on in the world and to be current with events, they are always seen on the internet reading, browsing, and reading fashion and social blogs. There is obvious a great decrease in student's passion to read for pleasure and enjoyment but instead, prefer to seek pleasure from the media by streaming videos on social media and playing with their Smart phones. The main reason why they now read is just to pass an examination and not to gain knowledge. This has reduced the vast use and development of the brain. Students are no more learning through reading. Students who so much devote their times on networking have a great tendency of having low grades, poor academic performance, and become unsuccessfull (Boyd and Elison, 2012).
The social media also have numerous positive impacts. Firstly, it enhances learning and education. Students, with the help of the Internet now have access to all form of information. Nothing is strange to 'Google'.
No matter how old the information is, the internet serves as search lights to them. Some information that cannot be found in the libraries and research centers are now available online. The use of search engines such as Google and Google Scholar has helped many students in their educational life (Harrasi, 2014).
Information technology is indisputable that a vast number of students have completely lost interest in reading, both in and out of higher institutions. To say that the reading competition and zeal among students are fast declining is simply stating the obvious(Dayo Adesulu, Adewole Adebusayo & Rebecca Amos, 2017). With the same fashion higher education institutions in Ethiopia have a great fear from excessive usage of social media by students than reading their academic subjects (Yirga, 2016). Due to this and other related facts, the researchers intended to conduct this research in Oda Bultum University.
2. b) Statement of the Problem
According to (Boyd and Ellison, 2017)social media is the connection of friends or family together which allows one to communicate easily. With media, one can have a long chain of friends' chat, or share information or ideas with many people virtually. Social networking sites can be defined as web-based services that allow individuals to construct a public or semipublic profile within a bounded system, articulate a list of other users with whom they share a connection, and view and traverse their list of connections and those made by others within the system.
Mostly basic level social networking sites allow users to set up online profiles or personal homepages, and develop an online social network. The profile page functions as the user's own webpage and includes profile information ranging from their date of birth, gender, religion, politics and hometown, to their favorite films, books quotes and what they like doing in their spare time. In addition to profile information, users can design the appearance of their page, and add content such as photos, video clips, music and files (Aljohani, 2016).
The popularity of social media in Ethiopia is rapidly increasing from time to time for a decade. This may be due to the students of colleges and universities as well as youth is widely used for global access. Social networking sites like Facebook, Imo, Telegram, Viber, WhatsApp, Twitter, Instagram, and YouTube have become a craze for everyone nowadays. In these cases, some students are more concerned about social media or social networks than on teaching by lecturers and will cause affected their academic performance (Abdi, 2018).
The negative effects of social networking sites overweight the positive. These sites have resulted in an impact of potential hazards to the community. The students are victims of social networks more often than others. This is because the consequences when they learn or find their course material online, they get attracted to these sites to kill their boredom in their studies and also distract them from their duties (Calancie, 2017).
Gaining access to the internet is still very difficult in Ethiopia, with internet penetration at just 15% for its over 105 million population. And even though over 53 million people have mobile connectivity, just 3.8 million of them are active social media users. Part of the problem is that data is expensive and not competitive, given the government's monopoly over all mobile and internet services through the state-owned Ethio Telecom (Ibid).
Through researchers' observation, mostly students in Oda Bultum University wasted much of their time in using social media than concentrating to study their academic subject matters. This excessive use of social media created addiction on students and resulted to reduce reading time of reference books and other academic materials. These and other related scenarios motivated researchers to conduct this research at Oda Bultum University.
3. c) Objective of the study i. General objective
The general objective of this study was to investigate effects of social media on studding habits of students; a case study at Oda Bultum University.
4. ii. Specific objectives
The specific objective of this study has been 1. To identify types of social media used by students in Oda Bultum university. 2. To explain benefits of social media usage in studying habits of students. 3. To measure time wasted and cost incurred by students in using social media. 4. To assess effect of social media usage in studying habits of students. 5. To suggest policy issues through possible recommendations drawn from the conclusion.
5. d) Scope of the study
This study covered Oda Bultum University students who are in sophomore and above class of year during 2018/19 academic year. The study was used both quantitative and qualitative data sources taken from students using semi structured questioner. The researchers followed mixed research method to make the analysis and the research was conducted on effect of social media on reading habits of students.
6. e) Significance of the study
The findings of this research output have many significances for academic institutions, government, non-government organizations, research institutes and policy makers to understand the effect and cost of social media on academic performance of students in higher education.
In addition to this, the findings of this research match benefited universities to develop regulations for systematic use of internet services. The University begins its operation by opening 7 colleges and 14 departments and currently reached at 9 colleges containing 34 departments in different streams.
7. II.
8. Research Methodology
9. b) Data Source and Type
For this research the researchers collected data from primary and secondary sources. The primary source of data was collected through questioner and secondary source of data were collected from books, internet and literatures related with social media.
10. c) Research Design and Strategy
The researchers used mixed research design methods through triangulation. The researchers were applied both qualitative and quantitative research design methods to collect the necessary data from respondents. To collect the required and necessary data the researchers distributed questioner and get filled through enumerators that were selected and trained about data collection strategies and methods. Furthermore, FGD were used to get further explanations from students about effects of using social media on reading habits.
11. d) Sampling Technique and Sampling Procedures
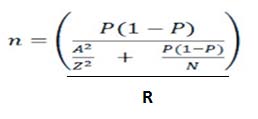
The researchers applied purposive research method to select Oda Bultum University to conduct the research. After that the researchers randomly selected 280students from the seven colleges using simple random sampling technique using probability proportion to sample size (PPSS).For this research the researchers selected 280 students from 1102students to conduct the research and to answer the research questions formulated. The 280 students were selected using Waste on sample size formula.
An Equation for determining Sample Size adapted from (Wasteon, 2001) Where
12. Result and Discussions
In this part of the paper, the researchers make data analysis and presentation using frequency tables, bar graphs, and charts. To answer the research questions, 280 questioners were distributed and collected from students that are following their regular classes within the university from 2 nd to 4 th year by the academic year of 2018/19.
After the questioners are collected, it was filled and coded using SPSS21 to make data analysis and presentation up on the specific objectives of the research title. As it is presented in Table 3.1. from total students selected to give responses on social media usage, 213 (76.1%) were males and the remaining 67 (23.9%) were females. In the above table from total 280 respondents, 245 (87.5%) answered that they do have a social media account and the remaining 35 (12.5%) answered that they did not have a social media account. This revealed that87.5% of students have access to different social media accounts within Oda Bultum University.
13. a) Background of the Respondents
From these respondents, 7 (2.5%) had age less than or equal to 17, 238 (85.0%) had age between 18-20 and the remaining 35 (12.5%) had age group between 21-23 respectively.
As a result, most students 213 (76.1) were males and also most of 238 (85.0%) of them were within the age group between 18-20. Thus, this result is in line with ministry of education report (MOE, 2018/19). As it is shown in the above table most students prefer to use Facebook account followed by YouTube account and very few students prefer to use WhatsApp within the university.
14. b) Types of Social Media used by students
Students participated in the FGD also asserted that most students preferred to use Facebook and followed by Telegram and IMO respectively. Most of them explained further that this social media account was preferred to exchange messages, assignments and also course materials with university students that are followed their education indifferent universities throughout the country. They also further explained that now a days; they prefer these accounts to follow political issues, ideas and other related messages that are disseminated using the accounts.
15. Source: Own Survey Result, 2019
16. Bar chart 1
As it is shown on the bar chart from total students asked to respond how to access and use the social media 240 students answered that they used the social media using their personal cellphone, 73 students explained that they used own laptop computer and the remaining 145 responded that they do have an access to social medias using desktop computers in computer laboratory of the university which is similar with (Cohen, 2011).
As a result most students in Oda Bultum university access social media accounts using their own cellphones using mobile data connectivity or using WIFI connections within the campus. Students also further explained during FGD that most of them are using WIFI connection of the university during both day and night time for different purposes around the library since the server is available around it without having proper sitting place and power connection for their cellphone. From total students asked to answer question related with social media usage for academic purpose, 220 (78.57%) responded that they used different social media accounts to do assignments given from instructors, 100 (35.71%) responded that they have been used to read reference materials, 230 (82.14%) responded that they have used to write senior essays, 15 (5.36%) students explained that the have been used to search scholarship opportunities and 115 (41.07%) responded that they used the social media to exchange documents using emails. Furthermore, other 70 (25.00%) students explained that they used social media accounts for other purposes.
17. i. Social Media Usage for Academic and Nonacademic Purpose
Students who are selected to respond about usage of social media for nonacademic issues; 150 (53.57%) responded that they used the social media to listen music and watching videos, 235 (83.93%) responded they used the social media to share /follow friend's posts and status updates at different periods, 125(44.64%) responded that they used to exchange sexual related messages and photos and for dating purposes, 30 (10.71%) responded that they used to exchange sexual related video contents and 45 (16.07%) explained that they have been used the social media for some other issues. Us it is shown in the above table, students waste minimum 2 hours and maximum of 12 hours in using the social media. The average time wasted by students in Oda Bultum university is found 6.10 hours and its standard deviation among students is 2.22 hours. Similarly based on students responded for the question about money wasted in suing social medias is found minimum of 3 birr and maximum of 15 birr per day and the average cost of using social media is 7.24 birr and the standard deviation is found 2.77 birr per day. This revealed that most students in Oda Bultum university wasted in using social medias 6.10 hours and 7.24 birr per day rather than studying their subject matter.
18. c) Time wasted and cost incurred by students in using social media
19. d) Benefits of using Social Media for Students
Source: Own Survey Result, 2019
20. Bar chart 2
From total students asked to explain about benefits of using social medias 245 answered that social media helps them to create contacts with their old friends and family members easily throughout the world and 180 students also explained that the benefits of using social media is to simply download and read educational materials. In addition to this, other 240 students responded that using social media benefited them in facilitation of sharing information and to follow posts about daily events their friends and other 220 students explained that the benefits of using social media is helping them to exchange educational and other documents through emails, face book, telegram and IMO.
Furthermore, students in the FGD explained that the benefits of using social media now a days helps them to follow activists about political issues and other related issues about national and regional affairs too. Most students further asserted in the FGD that university students using social medias to organize peaceful demonstrations too. From the total students who respond for effects of using social media 230 (82.14%) explained that using social media forced to reduce reading time for studying of their subject matter and other 200 (71.43%) students also explained that the effects of using social media affected to reduce their CGPA of students score from semester to semester.
21. e) Effects and Risks of using social media on Students Reading Habits
Moreover, from total students selected to respond for the above question 245 (87.5%) explained that using social media forced them to change their study time habits from the previous constant study time since they missed their previous proper study time to get internet access for social media usage at the WIFI area. Furthermore, 196 (70.00%) of students asserted that using social media have an effect of stress in time management on reading habits and other 150 (53.57%) of students explained using social media have other effects like illness on eyes and headaches due to extended time usage of social medias. Students are asked to explain risk associated with using different social medias. 245 (87.5%) students mentioned general addictions, 160 (57.14%) mentioned depression and anxiety, 120 (42.86%) explained unrealistic expectations, 30 (10.71%) mentioned cyber bulling, 65 (23.21%) mentioned fear of missing out and other 50 (17.86%) mentioned negative body image are some of the risks of using different social media.
22. IV. Conclusion and Recommendations a) Conclusion
Recently due to the advancement of technology, virtual communication become widely used type of communication throughout the world. As a result, most people in Ethiopia nowadays have his/her own cellphone to use this type of communication. Similarly, most students in Ethiopia have their own cellphone starting from secondary school for this type of communication.
Mostly these students utilize their cellphone to play games, to access social media accounts, and to make and receive calls from friends and family members. Students in Ethiopia dominantly used Facebook, YouTube, Telegram, Imo, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Viber to share messages and follow status updates of their friends.
Almost 87.71% of students in Oda Bultum universityused Facebook to follow status updates, to share photos, and messages of friends and relatives. Next to Facebook, students used YouTube to follow, watch, and share video contents through internet connection. To use these social media account, students wasted an average time of 6.10 hours per day and spent an average Ethiopian birr of 7.24 per day than following their academic class and studying subject matters.
Nowadays the worst scenario in Ethiopian universities for degradation of quality education is that, most students used social media accounts even to exchange assignments, project works, and senior essays from one university to the other with the same topic and content as their own original work rather than practicing for themselves. Furthermore, students begin to exchange exam answers during continuous assessment and final exam periods using social media accounts using their cellphone.
23. b) Possible Recommendations
Based on the findings of this research, the following possible recommendations are forwarded for further improvement: -? Universities should organize short term training to aware effects of using social media accounts on student's reading habits in each academic year in collaboration with the student union. ? Universities should develop mechanisms to have off periods for social media accounts access during class and study time within the campus in collaboration with the internet administrators. ? Ministry of science and higher education (MOSHE) should develop proclamations in collaboration with universities to discourage and penalize students directly coping assignments, project works, and exams using social media accounts. ? Universities should establish online repositories throughout the country to discourage direct copying of senior essays and project works.
24. RISKS OF USING SOCIAL MEDIA
| No. | Departments | No. of Students | PPSS |
| 1 | College of Agriculture | 223 | 57 |
| 2 | College of Agro Industry | 80 | 20 |
| 3 | College of Business and Economics | 244 | 62 |
| 4 | College of Natural and Computational Science | 144 | 37 |
| 5 | College of Natural Resource and Environmental Sciences | 188 | 48 |
| 6 | Institute of Technology | 153 | 39 |
| 7 | Institute of Land Administration | 70 | 17 |
| Total | 1102 | 280 | |
| Source: Oda Bultum university registrar report, 2018 | |||
| e) Method of Data Analysis | |||
| For this research the researchers applied | |||
| descriptive statistics to answer the research questions. | |||
| For data presentation, researchers used frequency | |||
| tables, graphs, charts, and percentages. Moreover, | |||
| researchers integrate FGD results with other data | |||
| collected from students using narration. | |||
| III. | |||
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| Male | 213 | 76.1 | 76.1 | 76.1 |
| Female | 67 | 23.9 | 23.9 | 100.0 |
| Total | 280 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| DO You have Social Media account | ||||
| Yes | 245 | 87.5 | 87.5 | 87.5 |
| No | 35 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 100.0 |
| Total | 280 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| Age of Respondents | ||||
| <= 17.00 | 7 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 18.00 -20.00 | 238 | 85.0 | 85.0 | 87.5 |
| 21.00 -23.00 | 35 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 100.0 |
| Total | 280 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| Source: Own Survey Result, 2019 | ||||
| Types of Social media accounts | Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent |
| 240 | 85.71 | 85.71 | 25.07 | |
| Telegram | 170 | 60.71 | 60.71 | 42.83 |
| 75 | 26.79 | 26.79 | 50.67 | |
| 42 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 55.06 | |
| IMO | 145 | 51.79 | 51.79 | 70.21 |
| YouTube | 200 | 71.43 | 71.43 | 91.11 |
| Viber | 85 | 30.36 | 30.36 | 100.00 |
| Total | 280 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| Source: Own Survey Result, 2019 | ||||
| From those respondents who responded that | ||||
| they do have social media account 240 (85.71%) | ||||
| explained that they do have Facebook account, 170 | ||||
| (60.71%) have Telegram account, 75 (26.79%) do have | ||||
| Instagram, 42 (15%) do have WhatsApp, 145 (51.79%) | ||||
| do have IMO, 200 (71.43%) do have YouTube and other | ||||
| respondents explained that 85 (30.36%) do have Viber. | ||||
| For academic Purpose (Multiple Response) | Frequency | Percent |
| To do assignments | 220 | 78.57 |
| To read reference materials | 100 | 35.71 |
| To write senior essays | 230 | 82.14 |
| To search scholarships and funding | 15 | 5.36 |
| To exchange email | 115 | 41.07 |
| For other purpose | 70 | 25.00 |
| Total | 280 | 100.0 |
| For Nonacademic Purpose (Multiple Response) | ||
| To listen music and watching videos | 150 | 53.57 |
| To share/follow friends' posts & status updates | 235 | 83.93 |
| TO exchange sexual related messages and photos | 125 | 44.64 |
| To exchange sexual related videography contents | 30 | 10.71 |
| For other purposes | 45 | 16.07 |
| Total | 280 | 100.0 |
| Source: Own Survey Result, 2019 | ||
| Descriptive Statistics | ||||
| N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation |
| Effects of using Social Media on students Reading Habits | Frequency | Percent |
| Forced to reduce reading time for studying | 230 | 82.14 |
| Affected my cumulative CGPA | 200 | 71.43 |
| Forced to change my study time | 245 | 87.5 |
| Creates stress in time management | 196 | 70.00 |
| Other effects | 150 | 53.57 |
| Total | 280 | 100.0 |
| Source: Own Survey Result, 2019 | ||